Carnosine: The Athletes’ Secret to Greater Gains
About Carnosine: Science, Sources, and Benefits
Carnosine is a dipeptide or compound made up of two linked amino acids: beta-alanine and histidine. This compound is found in the active tissues of the body, including the muscle, the heart and the brain. Carnosine levels play a critical role in muscle strength and performance.
The Science Behind Carnosine
Carnosine increases performance in many aspects including improving brain health and heart health, which improve performance as a consequence. One of the most unique roles of carnosine is in muscle cells; a buffering agent to maintain muscle functions.
The body breaks down glucose through a metabolic process known as glycolysis. Glucose is the primary source of energy for exercise. When the intensity of a workout increases, equal amounts of lactate and hydrogen ions become the major end-products of glucose metabolism.
Throughout a workout, hydrogen ions can be actively transported from the muscle cells and into the circulatory system. However, at higher exercise intensities, the rate of hydrogen ion production becomes increasingly insufficient. Highly reactive hydrogen ions cause a fall in pH in the muscles, a process referred to as acidification.
Carnosine Buffers the Onset of Fatigue
As acidity rises and the muscle pH falls, fatigue sets in. The formation of cross links between proteins responsible for power generation and shortening of the muscle fibers can become compromised. Carnosine buffers that pH decline, and keep muscle working.
High concentrations of carnosine result in more effective buffering, greater muscle elasticity, and a delay—or prevention—of muscle fatigue. For athletes, the less fatigue, the greater the gains.
Why is it Ineffective to Ingest Carnosine Directly?
Simply put, carnosine isn’t effectively absorbed when taken directly. Orally-ingested carnosine breaks down into beta-alanine and histidine in the bloodstream after absorption. Only micro amounts of carnosine actually make their way into the bloodstream.
Research has shown that enough histidine is naturally present in the body to meet the demands of muscles for the synthesis of carnosine. Turns out, the key ingredient for increasing carnosine isn’t carnosine itself, but beta-alanine
Achieving Optimal Carnosine Levels
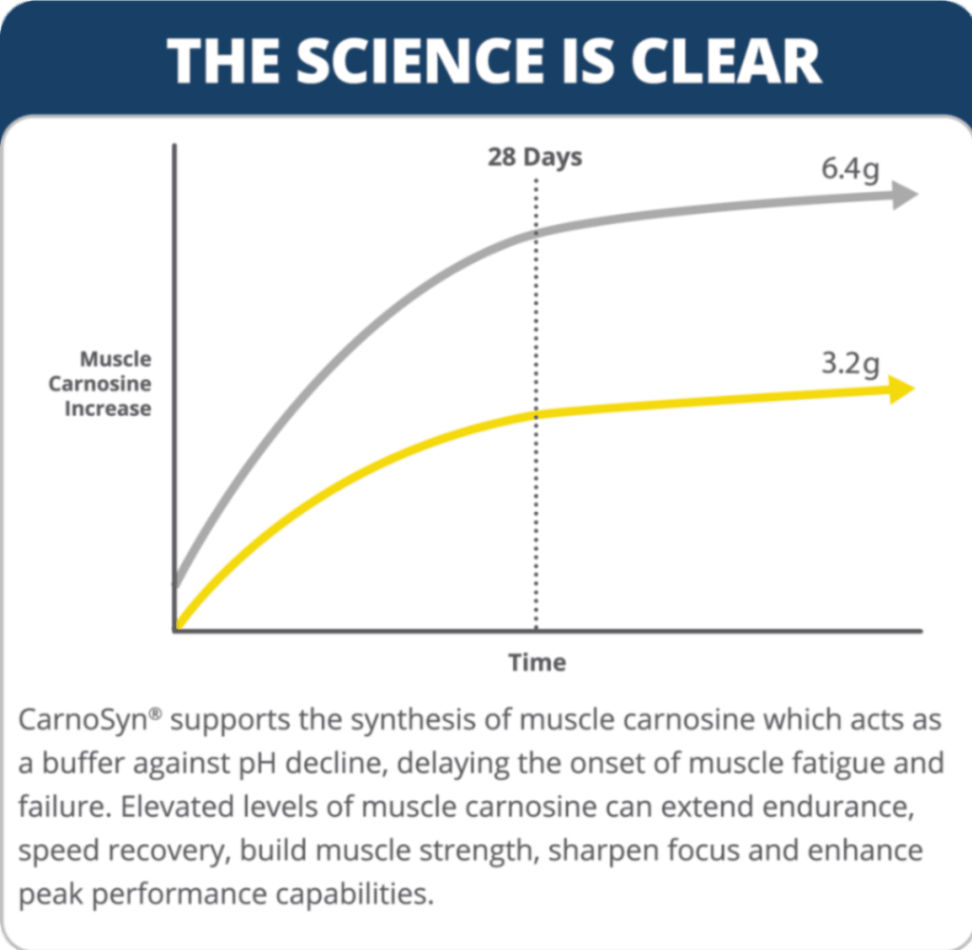
Beta-alanine is often referred to as the catalyst for achieving optimal carnosine levels. This non-proteinogenic amino acid supports the synthesis of muscle carnosine in the body. Taking beta-alanine daily—not just on workout days—maintains those optimal levels.
Supplementing with the right dosage of beta-alanine is critical. 3.2 grams daily over 28 days is the threshold for reaping the benefits of beta-alanine. For increased performance, athletes load an average of 6.4 grams per day.
The CarnoSyn® Discovery
Athletes have one particular individual to thank for advancements in performance through supplementation—Dr. Roger Harris. After years of researching and patenting the benefits of creatine for muscle building, Dr. Harris turned his attention to beta-alanine and carnosine.
When he began testing ways to increase muscle carnosine, Dr. Harris discovered that CarnoSyn® beta-alanine combined with histidine to form muscle carnosine. More research has determined that the limiting factor was the level of CarnoSyn® beta-alanine. It turned out that most normal diets provide enough histidine but not include enough naturally occurring beta-alanine to boost carnosine production and increase athletic performance.
There are over 55 clinical studies support the athletic performance benefits of CarnoSyn® beta-alanine. Patented, pure, and banned substance free, CarnoSyn® is certified by national and international agencies for its safety and efficacy.
As the go-to ingredient for sports nutrition formulations, CarnoSyn® helps athletes build better muscle, faster. To purchase CarnoSyn® Verified products, visit www.carnosyn.com/find-carnosyn.